Net Metering in a Solar Energy System: Everything You Need to Know
With the growing adoption of solar energy, net metering has emerged as a crucial mechanism that benefits both domestic and corporate consumers. It allows solar panel owners to efficiently manage their energy consumption, reduce electricity bills, and contribute to a greener grid. This system plays a key role in making solar power adoption more attractive and financially viable. Here’s everything you need to know about net metering and how it can benefit you.
What is Net Metering?
Net metering is a billing arrangement that enables solar energy system owners to send excess electricity generated by their solar panels back to the grid in exchange for credits. These credits can be used to offset electricity drawn from the grid when solar generation is low, such as during nighttime or cloudy days. Essentially, it acts as a virtual battery, allowing consumers to bank the excess energy they generate and use it when needed.
How Does Net Metering Work?
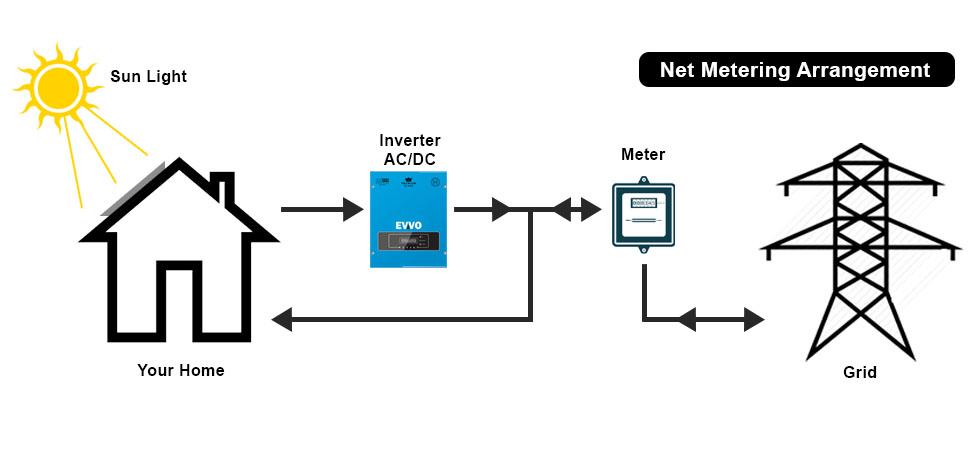
- Solar Generation: Solar panels generate electricity, which is used to power on-site appliances and equipment.
- Excess Energy Export: If the solar system produces more electricity than needed, the surplus is fed into the grid through a bidirectional meter.
- Credit Accumulation: The exported electricity is credited to the consumer’s account by the utility provider, typically at a predefined tariff rate.
- Grid Import: When solar production is insufficient (such as at night or on cloudy days), the consumer can draw electricity from the grid, using the previously earned credits to offset costs.
- Billing Settlement: At the end of the billing cycle, consumers are charged only for the net electricity used (i.e., grid consumption minus solar export credits).
Benefits of Net Metering
For Domestic Consumers
- Lower Electricity Bills: Homeowners can significantly reduce their monthly electricity expenses by using solar energy and receiving credits for excess power.
- Energy Independence: Households relying on solar energy reduce their dependence on traditional utility companies, protecting against rising electricity rates and power outages.
- Environmental Impact: By feeding clean energy back into the grid, residential consumers contribute to reducing carbon emissions and promoting renewable energy adoption.
- Return on Investment: The payback period for solar panels is shortened as homeowners can monetize excess energy, making their investment more financially rewarding.
For Corporate Consumers
- Operational Cost Savings: Businesses with large rooftop solar installations can cut down on energy costs and improve financial sustainability.
- Sustainability Goals: Many corporations are integrating net metering into their ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) strategies to achieve carbon neutrality and improve their green credentials.
- Enhanced ROI: Net metering increases the return on investment (ROI) for solar power installations by ensuring that surplus energy is utilized effectively, maximizing financial benefits.
- Compliance with Renewable Energy Mandates: Many corporate entities must comply with renewable energy regulations, and net metering helps them meet their sustainability targets efficiently.
Net Metering Policies in India
The Indian government has introduced various net metering policies to encourage solar adoption. Policies may vary by state, but key features include:
- Eligibility: Available for residential, commercial, and industrial consumers with rooftop solar installations.
- Credit System: Credits are adjusted against future electricity bills, reducing the consumer’s overall energy costs.
- Capacity Limits: States may impose limits on the maximum solar capacity eligible for net metering, typically ranging from 1 kW to 1 MW, depending on regulations.
- Settlement Mechanism: Some states allow credit rollover to the next billing cycle, while others may compensate excess power at a predetermined feed-in tariff.
- Connection Agreements: Consumers must sign agreements with local distribution companies (DISCOMs) to ensure compliance with net metering policies.
Challenges and Considerations
While net metering provides numerous advantages, there are some challenges to consider:
- Policy Variability: Net metering regulations differ across states, requiring consumers to stay informed about local policies and potential policy shifts.
- Technical Limitations: The grid infrastructure must support bidirectional energy flow, which may require upgrades to prevent instability.
- Cap on Credits: Some states have limits on how much surplus energy can be credited or carried forward, reducing financial benefits.
- Grid Reliability: Large-scale adoption of net metering can put pressure on the grid, requiring advanced grid management solutions.
- Utility Resistance: Some utility companies may resist net metering due to reduced revenues, leading to policy pushback or unfavourable rate structures.
Steps to Avail Net Metering
- Assess Your Solar Potential: Conduct a feasibility study to determine your solar generation capacity and energy needs.
- Check Local Policies: Verify net metering eligibility and regulations with your state’s electricity board or utility provider.
- Install a Net Metering-Enabled System: Work with a certified solar installer to set up a system that complies with net metering guidelines.
- Apply for Net Metering: Submit an application to the local DISCOM for net metering approval, including required documentation.
- Install a Bidirectional Meter: Utilities may require the installation of a special meter that tracks both energy import and export.
- Monitor Your Consumption and Credits: Use monitoring tools or utility-provided statements to track your energy credits and optimize usage.
Conclusion
Net metering is a game-changer for both residential and corporate consumers, making solar energy adoption more financially viable and environmentally sustainable. By leveraging this system, consumers can maximize the benefits of their solar installations while contributing to a greener energy future.
For businesses and homeowners considering solar energy, understanding and utilizing net metering can lead to significant cost savings and a lower carbon footprint. Be sure to check with our expert team on sales@carbonculture.co to understand the specific net metering policies applicable in your region. With the right approach, net metering can be an integral part of achieving energy efficiency and sustainability goals.
Sources of Data Used in This Blog
- Ministry of New and Renewable Energy (MNRE), Government of India (www.mnre.gov.in)
- Central Electricity Authority (CEA), India (www.cea.nic.in)
- State Electricity Regulatory Commissions (SERCs) reports and guidelines
- International Energy Agency (IEA) reports on solar energy adoption trends
- Industry insights from solar power providers and energy consultants
- Research papers and case studies on net metering and distributed energy systems